
Since the inter nuclear distance between two bonded atoms is called the bond length. Therefore, R covalent = ½ (internuclear distance between two bonded atoms) It is defined as one half the distance between the nuclei of two covalently bonded atoms of the same element in a molecule. The distance from the centre of the nucleus to the point up to which the density of the electron cloud is maximum. The distance from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost shell containing electrons. The properties which are directly or indirectly related to their electronic configuration and which show a regular gradation when we move from left to right in a period or from top to bottom in a group are called periodic properties. Since the electronic configuration of the elements are a periodic function of their atomic numbers therefore these atomic properties are also a periodic function of atomic number of the elements. the properties of a collection or a group of atoms and are only indirectly related to the electronic configuration.Īll these properties which are directly or indirectly related to the atomic structure or the electronic configuration of the elements are called atomic properties. This citation format is based on MLA.Properties like melting point, boiling point ,heat of fusion and vaporisation, energy of atomisation, density ,atomic volume are the bulk properties i.e. Also replace URL for the actual url of this page (The stay, ok?). Now replace dd, mmmm and yyyy with the day, month, and year you browsed this page. "Atomic Radius of Chlorine (Cl) [& State, Uses, Discovery.
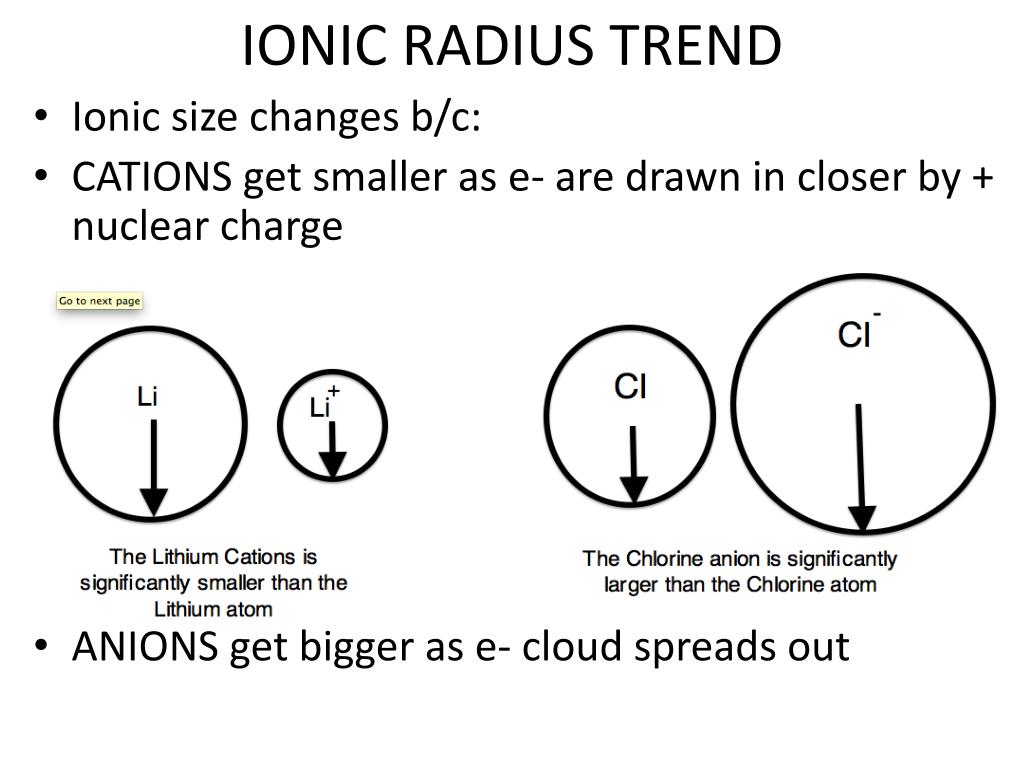
To make your life (and citation) easier just copy & paste the information below into your assignment or essay: That gives credibility to your paper and it is sometimes required in higher education. CitationWhen you need to include a fact or piece of information in an assignment or essay you should also include where and how you found that piece of information. How about an incentive to share this post? (You will help other colleagues find this blog)ĭownload and enjoy this complete and colored periodic table for you to edit and enjoy. Need an editable periodic table to edit? Maybe add your school logo, work team or anything else to make your paper look cool?Īlong with basic atom / element information (like Chlorine atomic radius and all the other atomic data), it also comes with color coded info about: State (Gas, Liquid or Solid at room temperature), Groups/series details and much more. How a small number of atoms can be joined and form completely different substances.Video Are you having trouble understanding the basics of atomic elements? This video will walk you through: Want to learn more details and data about Chlorine (Cl)? Check my Elements Comprehensive List. Name OriginGreek: chlôros (greenish yellow).ĭiscoveryDiscovered By: Carl Wilhelm Scheele Commercial quantities are produced by electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride (seawater or brine from salt mines).ĭescriptionGreenish-yellow, disagreeable gas. SourcesSalt (sodium chloride, NaCl) is its most common compound. UsesUsed in water purification, bleaches, acids and many, many other compounds such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFC). In the case of Chlorine the atomic radius is 0.97 Å. There are cool facts about Chlorine that most don't know about. Note: Learn more about the atomic radius here. Ok, so what is the atomic radius of an atom of Cl? All atoms have a (theoretical) atomic radius, even Chlorine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
